- Log in to:
- Community
- DigitalOcean
- Sign up for:
- Community
- DigitalOcean

Introduction
We love what Allen AI is doing to lower the barrier to entry, empowering university labs, independent researchers, and hobbyists to contribute to the next generation of AI. What we’re referring to are their open-source releases, particularly Olmo 3, which we will flesh out in this article. The Olmo 3 paper provides comprehensive access to models, datasets, code, training logs, and live demos. This level of transparency and accessibility is exceptionally rare in the field.

Prerequisites
This article assumes familiarity with LLM training (e.g., pretraining, post-training). For a comprehensive overview of LLM training, we recommend The Smol Training Playbook from Hugging Face.
The goal of this article is to give you a relatively concise overview of Olmo3 so that you can quickly get your hands dirty with implementation.
We hope that showcasing the material in tables will give you a comprehensive birds-eye view of this release, which is already explained comprehensively in:
- Olmo 3 and the Open LLM Renaissance by Cameron R. Wolfe
- Olmo 3: Charting a path through the model flow to lead open-source AI | Ai2 (Allen AI’s Olmo 3 launch post)
- Nathan Lambert’s Olmo 3 Lecture
Additionally, feel free to reference the Olmo 3 Technical Report alongside this article to give you additional context on the model spec and training pipeline. Familiarity with Olmo 2 may be helpful, as Olmo 3 builds upon its previous iteration.
Key Takeaways
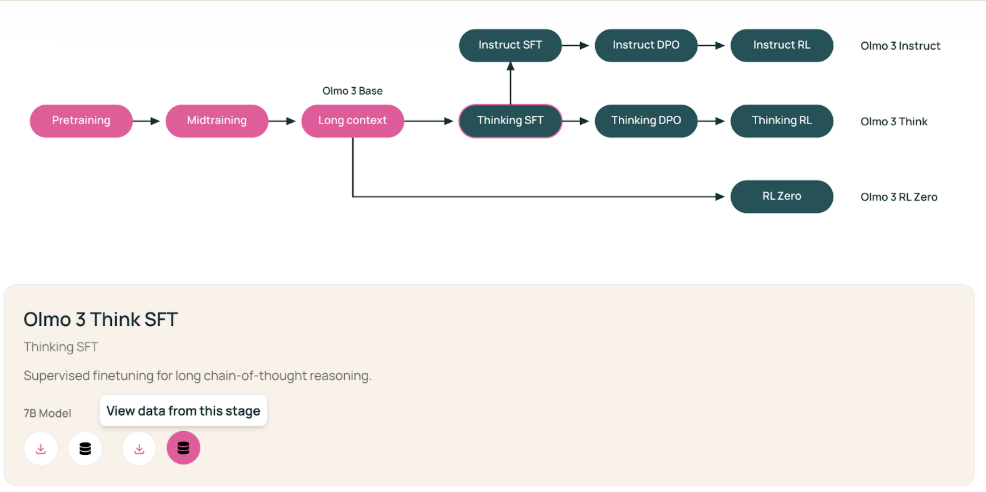
- The Olmo 3 base model underwent pretraining on a general text corpus (dolma 3 mix), midtraining with targeted & high quality data (dolma 3 dolmino), and context extension (dolma 3 longmino)
- Post-trained models include Olmo 3 Instruct, Olmo 3 Think, and Olmo-3 RL-Zero.
- AI2 provides integration of Olmo3 with OlmoTrace, a tool that lets you see how model outputs connect back to specific pretraining data.
The model was pretrained with Dolma3 and post-trained with the Dolci suite.
Model Architecture
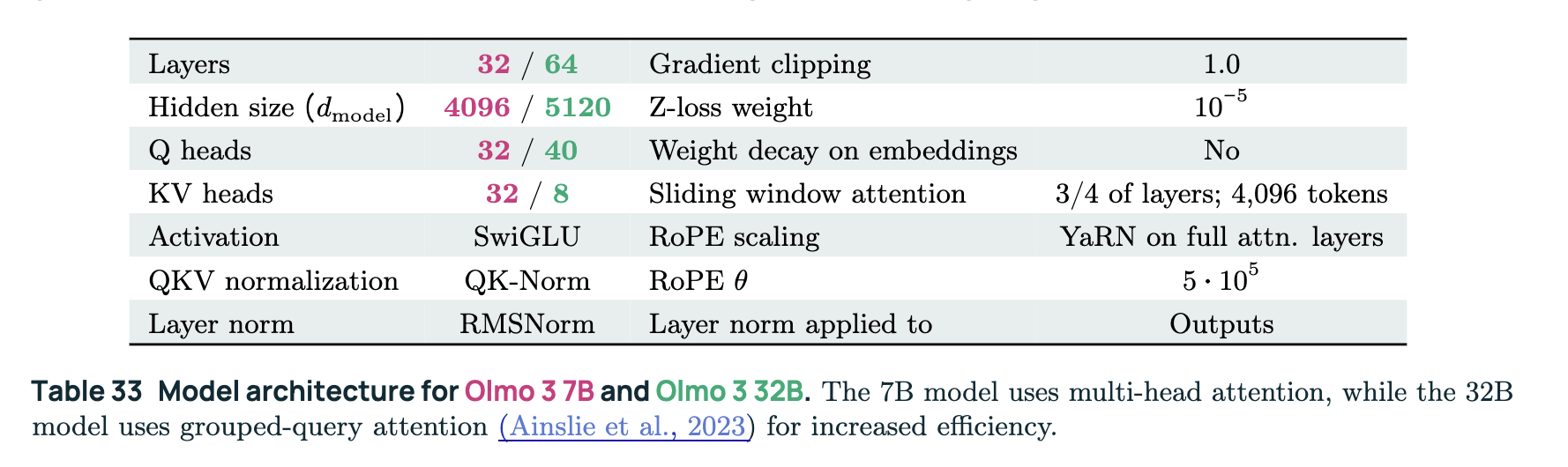
In the table below, we outline key features of the Olmo 3 architecture.
| Spec | Relevance |
|---|---|
| 7B and 32B Parameters | Olmo 3 is available in two versions: 32B and 7B parameters. Model Layers Hidden size (dmodel) Q heads KV heads 32B 64 5120 40 8 7B 32 4096 32 32 Notice how the 7B model has the same number of Query (Q) and Key-Value (KV) heads whereas the 32B model has substantially more Q heads than KV. This is because the 32B model is using grouped query attention (GQA) whereas the 7B model is using multi-head attention (MHA). For a primer on attention, check out the attention and its variants section in our LLM inference optimization article. The model is compact and efficient enough to run on high-end consumer GPUs (7B) or single research nodes (32B). |
| Dense Transformer | While we’ve been historically seeing many open weight models using MoE (e.g., Kimi-K2, gpt-oss), Olmo 3 uses a dense, decoder-only transformer architecture. |
| Sliding Window Attention (SWA) | The researchers introduce a sliding window attention (SWA) pattern to enable scalable pretraining at extended sequence lengths while maintaining manageable inference costs. In this approach, each token attends to preceding tokens within a window of 4096 tokens. The researchers apply SWA to three out of every four layers and ensure the final layer consistently employs full attention. |
| Rotary Position Embeddings Θ = 5e5 | RoPE encodes position through the rotation of the query and key vectors depending on the token’s position.The encoding of position is critical since attention is order-blind to the input tokens. In this case, they See figure 13 in the Olmo3 paper to get a sense of how RoPE’s theta value of 500K is the primary contributor to scores on the RULER benchmark. |
| YaRN | YaRN (Yet another RoPE-scaling method) is a compute-efficient technique designed to efficiently extend the context window of transformer-based models. The researchers tried several methods for extending RoPE beyond the original pretraining context length (see section 3.6.4). They found that applying YaRN only to full attention layers yields the best performance. |
Data Curation
| Dataset Name | Size | Description & Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Dolma 3 | ~9.3 trillion tokens | The full corpus drawn from web pages, science PDFs, codebases, math problems, and encyclopedias. |
| Dolma 3 Mix | 5.9 trillion tokens (~6T) | A pretraining mix constructed from Dolma 3. It features higher proportions of code and math data with strong decontamination/deduplication. allenai/olmo-3-pre-training |
| Dolma 3 Dolmino | 100 billion tokens | The mid-training mix constructed from Dolma 3. It focuses on high-quality math, science, code, and reading comprehension to enhance specific skills before final tuning. allenai/dolma3_dolmino_pool |
| Dolma 3 Longmino | ~50 billion tokens | The long-context mix constructed from Dolma 3. It combines long documents (from a 639B pool) with mid-training data to teach the model to track info over long inputs (up to 65K tokens). allenai/dolma3_longmino_pool |
| Dolci Suite | Variable (Mix dependent) | The post-training data suite. It contains distinct mixes for SFT (reasoning/tool use), DPO (contrastive preference), and RLVR (verifiable rewards). allenai/olmo-3-post-training |
| Function / Stage | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Pretraining | Pretraining | The initial phase consists of three sub-steps: broad capability learning, mid-training (skill sharpening), and long-context extension. |
| SFT | Post-Training | Supervised Fine-Tuning. Used to align the model’s raw output into specific formats (e.g., chat, step-by-step thinking). |
| DPO | Post-Training | Direct Preference Optimization. A tuning method where the model learns from preference data (choosing “better” answers over “worse” ones). |
| RLVR | Post-Training | Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards. A specialized RL stage used to elicit high-quality reasoning traces by rewarding verifiable correct outcomes (e.g., in math or code). |
OlmoTrace
OlmoTrace lets users highlight text and trace it back to its source in the training data. This helps audit hallucinations, detect contamination (distinguishing reasoning from memorization), and study scaling laws by tracking how reasoning emerges with more training data and compute.
Olmo3 on DigitalOcean
DigitalOcean has GPU Droplets which you can use to tinker with these models.
The Olmo3 blog post features an interactive figure which allows you to see the training stage and associated datasets.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Olmo-core | A state-of-the-art framework for distributed model training. A pre-training codebase designed to maximize efficiency. Docs: OLMo-core v2.4.0 |
| Open Instruct | Post-training pipeline |
| datamap-rs | Pure-Rust toolkit for large-scale cleaning |
| duplodocus | For ultra-efficient fuzzy de-duplication |
| OLMES | A toolkit for reproducible evals. It includes our brand-new eval collection OlmoBaseEval, which we used for Olmo 3 base model development |
| decon | Removes test sets from training data |
References and Additional Resources
Olmo 3 | Livestream with Hugging Face
How We Built a Leading Reasoning Model (Olmo 3)
Olmo 3: Charting a path through the model flow to lead open-source AI | Ai2
The Big LLM Architecture Comparison by Sebastian Raschka
LLMs-from-scratch/ch05/13_olmo3/standalone-olmo3.ipynb at main
Olmo 3 and the Open LLM Renaissance by Cameron R. Wolfe
FAQ
Why did the researchers use hybrid sharded data parallel (HSDP)?
The Olmo 3 team used Hybrid Sharded Data Parallel (HSDP) primarily to improve training efficiency and scalability. HSDP combines the benefits of Fully Sharded Data Parallel (FSDP) within each node and standard Data Parallelism across nodes. This approach reduces inter-node communication overhead, which is especially important at large scales, and allows for more efficient synchronization of parameters and gradients during model updates. By restricting communication-intensive operations to within-node, HSDP enables better scalability and faster training for large models like Olmo 3 Base
How was data curated for Olmo 3?
| Stage | Key Data Sources | Processing Highlights | Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pretraining | Common Crawl [A.2.1], olmOCR PDFs, Stack-Edu (code), arXiv, FineMath, Wikipedia/Wikibooks. | Deduplication (hash/MinHash) [A.2.2], quality filtering (fastText), token-constrained mixing, upsampling high-quality data. | Build a diverse, high-quality foundation (6T tokens). |
| Midtraining | Synthetic math (TinyMATH, CraneMath), code (Stack-Edu, Nemotron), QA (Reddit-to-Flashcards), reasoning traces. | Microanneals for dataset testing, integration tests, decontamination, intentional inclusion of instruction/thinking data. | Boost math, code, reasoning, and QA capabilities (100B tokens). |
| Long-Context Extension | olmOCR PDFs (long documents), synthetic aggregation tasks. | Document filtering (gzip), packing, intra-document masking, YaRN for positional embeddings. | Enable 65K-token context with long-form documents (50B–100B tokens). |
| Post-Training (Think) | Reasoning traces (OpenThoughts3, SYNTHETIC-2), math/code/chat prompts, DPO pairs [4.3.1] (Qwen3 models). | SFT/DPO/RL stages, verifiable rewards, delta-learning for contrastive pairs. | Optimize for reasoning (math, code, chat) and precise instruction-following. |
| Post-Training (Instruct) | Function-calling data, WildChat, precise IF prompts, multi-turn DPO, length-controlled responses. | Focus on usability, tool-use, and concise outputs; RL for general chat and function-calling. | Optimize for chat usability, tool integration, and brevity. |
| Post-Training (RL-Zero) | Filtered math (DAPO, Omega), code/IF/chat subsets, decontaminated evals. | RL-from-scratch with verifiable rewards; simple prompt templates. | Benchmark RL algorithms with transparent, contamination-free data. |
Final Thoughts
Olmo 3 is an impressive release. The model’s three-stage training pipeline (pretraining on Dolma 3 Mix, midtraining on Dolma 3 Dolmino, and long-context extension on Dolma 3 Longmino) has produced a suite of post-trained models, including Instruct, Think, and RL-Zero, optimized for different capabilities. We’re excited to hear about how people take advantage of the access to models, datasets, code, and training logs.
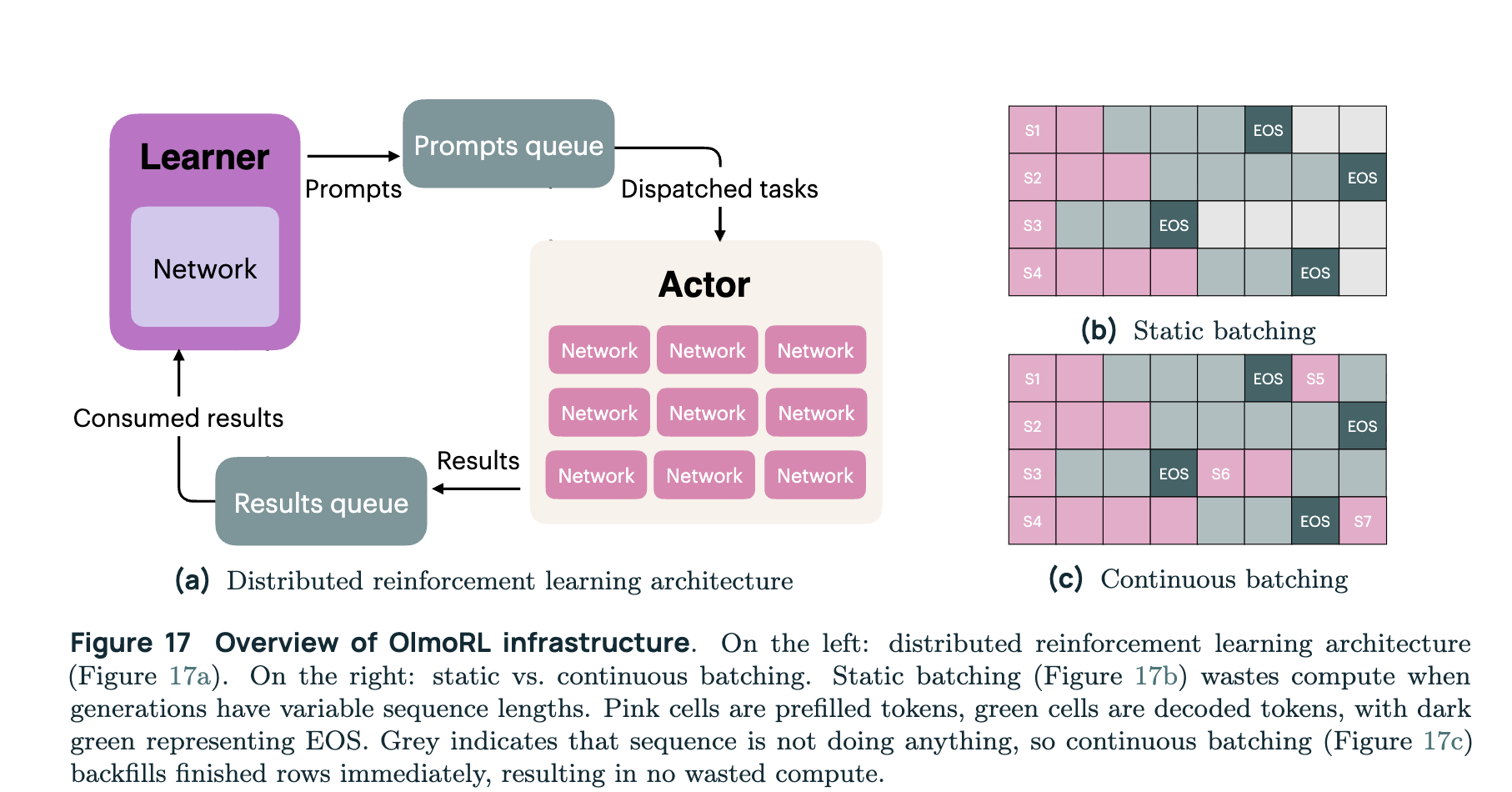
How did the researchers make RL training 4x more efficient?
The researchers incorporated in-flight weight updates AKA pipeline RL, continuous batching (dynamic prompt replacement to avoid GPU idle time), and a lot of threading improvements.
Thanks for learning with the DigitalOcean Community. Check out our offerings for compute, storage, networking, and managed databases.
About the author
Melani is a Technical Writer at DigitalOcean based in Toronto. She has experience in teaching, data quality, consulting, and writing. Melani graduated with a BSc and Master’s from Queen's University.
Still looking for an answer?
This textbox defaults to using Markdown to format your answer.
You can type !ref in this text area to quickly search our full set of tutorials, documentation & marketplace offerings and insert the link!
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Key Takeaways
- Model Architecture
- Data Curation
- OlmoTrace
- Olmo3 on DigitalOcean
- References and Additional Resources
- FAQ
- Final Thoughts
Deploy on DigitalOcean
Click below to sign up for DigitalOcean's virtual machines, Databases, and AIML products.
Become a contributor for community
Get paid to write technical tutorials and select a tech-focused charity to receive a matching donation.
DigitalOcean Documentation
Full documentation for every DigitalOcean product.
Resources for startups and SMBs
The Wave has everything you need to know about building a business, from raising funding to marketing your product.
Get our newsletter
Stay up to date by signing up for DigitalOcean’s Infrastructure as a Newsletter.
New accounts only. By submitting your email you agree to our Privacy Policy
The developer cloud
Scale up as you grow — whether you're running one virtual machine or ten thousand.
Get started for free
Sign up and get $200 in credit for your first 60 days with DigitalOcean.*
*This promotional offer applies to new accounts only.
